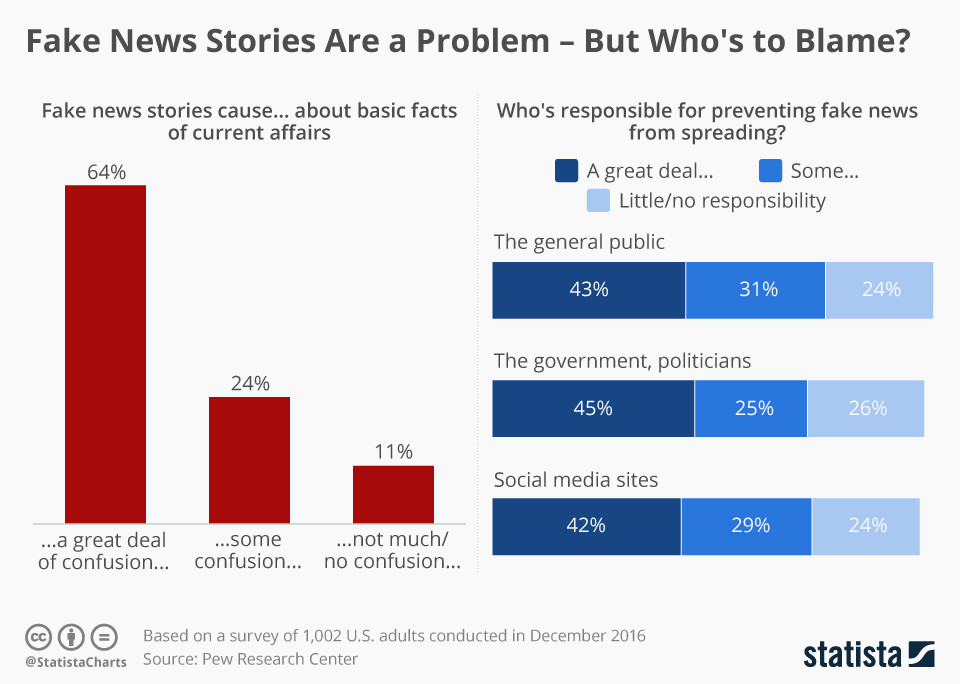
Fake News Spreads Faster than Real News on Twitter
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) looked at more than 126,000 stories tweeted millions of times between 2006 and the end of 2016. Researchers revealed that Twitter is an excellent platform for spreading actual news but unfortunately, the analysis shows, it's even better at spreading fake news. The analysis of stories tweeted by 3 million people shows that false news spreads substantially faster on Twitter than true news.

Do you have similar website/ Product?
Show in this page just for only
$2 (for a month)

0/60
0/180
Fake News Spreads Faster than Real News on Twitter



Twitter is an online news and social networking service where users post and interact with messages, known as ?tweets?. Though the lengths of the tweets are restricted to 280 characters still they are enough for people to put up their opinions. Twitter is an excellent platform for spreading actual news but in a recent study it has been confirmed that fake news spreads faster than real news on twitter.

Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) looked at more than 126,000 stories tweeted millions of times between 2006 and the end of 2016. Researchers revealed that Twitter is an excellent platform for spreading actual news but unfortunately, the analysis shows, it's even better at spreading fake news. The analysis of stories tweeted by 3 million people shows that false news spreads substantially faster on Twitter than true news.
They found that fake news spread through Twitter reaches farther, faster, deeper and more broadly than the truth in all categories of information.
"Falsehood diffused significantly farther, faster, deeper, and more broadly than the truth in all categories of information," wrote Soroush Vosoughi and Deb Roy of the MIT Media Lab and Sinan Aral of MIT's Sloan School of Management. The trio reported their findings this week in the journal Science.
"It took the truth about six times as long as falsehood to reach 1,500 people," the researchers added.

It was also revealed that, compared to tweets about claims that were verifiably true, tweets about claims that were false were 70% more likely to be retweeted. And false claims about politics spread further than any other category of news included in the analysis.
The researchers considered news to be any asserted claim made on Twitter that claim could be expressed in words, a photo or a link to a full article on the internet.
How the researchers came to this conclusion?
The scientists found out that when any type of news claim spreads on Twitter, it becomes a "rumor."The pattern by which a particular tweet spreads is a "rumor cascade." If a tweet is retweeted 10 times in an unbroken chain, it is a single cascade with a size of 10. If two people independently tweet the same piece of news and each of those tweets is retweeted five times in an unbroken chain, we have two rumor cascades, each of size five.

Vosoughi, Roy and Aral used this framework to map the spread of information on Twitter, they mapped out every single rumor cascade rooted by a claim that had been fact-checked by snopes.com, politifact.com, factcheck.org, truthorfiction.com, hoax-slayer.com or urbanlegends.about.com. They wound up with roughly 126,000 rumor cascades for their analysis.
For each cascade, the researchers determined the number of people involved in the cascade from start to finish, the number of retweets in a single, unbroken chain, the largest number of people who were part of the cascade at any depth, and the measure of the number of people who were responsible for helping a particular tweet spread.
The Results
? Tweets containing false news were typically retweeted by "many more people" than tweets containing true news.
? The time it took for a claim to reach 1,500 people on Twitter was about six times longer for true news than it was for false news.
? False news was also more likely to be "viral." So not only were the retweets chains longer, but they were more likely to branch off into new chains.

? The time it took for a rumor cascade to achieve a depth of 10 was about 20 times longer for true news than it was for false news.
? Rumor cascades about politics outnumbered those of all other topics. Coming in second were cascades about urban legends, followed by ones about business, terrorism, science, entertainment and natural disasters.
? Fake news about politics spread to 20,000 people almost three times more quickly than any other kind of false news was able to reach just 10,000 people.
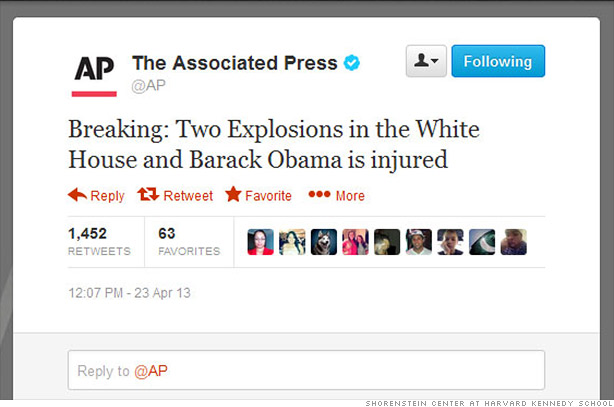
During the 2016 U.S. presidential election, the internet was abuzz with discussion when reports surfaced that Floyd Mayweather wore a hijab to a Donald Trump rally, daring people to fight him. The concocted story started on a sports comedy website, but it quickly spread on social media?and people took it seriously.

This scenario reveals that how much of a chaos can the fake spread on social media can create. Social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, etc need to take more strict measures to minimize the spread of fake news.
CONTINUE READING
Technology
International
News
Sandeep Semwal
Content Writer
