Looping in #C : For loops and their uses in programs (module 23)
In this section we will learn on the topic and concepts of loops, it's uses in programs. Types of loops, while loops, do-while loops, for loops etc

Do you have similar website/ Product?
Show in this page just for only
$2 (for a month)

0/60
0/180
This is the 23rd module on learning C with us. Earlier we discussed on the basic introduction and structure of C, preprocessor it's features, intermediate and executable codes. compilation and execution process of a C program. And keywords and identifiers, data types, variables and constants, scope of variables, operators and expressions in C. Type casting in #C. Introduction to input and output functions and reading a character in #C. Unformatted and formatted input functions. Branching statements like if, if-else, nested if-else.
In this section we will learn on the topic and concepts of loops, it's uses in programs. Types of loops, while loops, do-while loops, for loops etc.
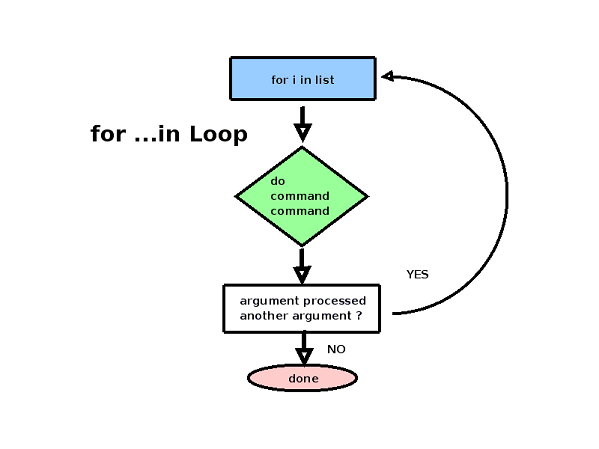
For loops :-
It is an iteration statement which is similar to while statement but this statement contains three expressions first one is initializing the loop counter, second expression is the condition and third one is loop counter increment/decrement. This statement first initialize the loop counter and then test the given condition in the beginning of the block, if the condition is true then the statements inside the block are executed, and the counter increment works.
If the condition is false then the statements after the block are executed. This statement is called as entr controlled loop.
The general form of for statement is :
for(initialize loop counter;test condition;increment/decrement)
{
do this;
and this;
}
Example :
|
In next module we will continue our discussions on the next topic. For more information regarding #C please be updated with us only on Www.newsandstory.com as we provide all the information on all the topics covered in #C.
CONTINUE READING
programming
learning
coding
technology
Dalpat I
Content writer
