What is Perfect Competition in Economics?
Here we understand about what is perfect competition, its meaning and features in Economics.

Do you have similar website/ Product?
Show in this page just for only
$2 (for a month)

0/60
0/180
What is Perfect Competition in Economics?
Definition of Perfect Competition:
"A market in which there is large number firms producing identical product so that no firm is powerful enough to influence the market price through individual actions."
Conditions or Features of Perfect Competition: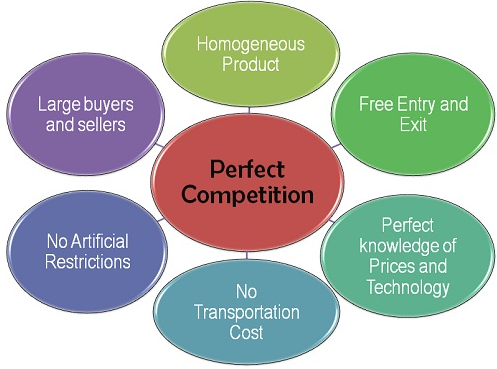
Perfect competition prevails when the following conditions are fulfilled:
- Large Number of Buyers and Sellers : The first condition of perfect competition is that there is a large number of buyers and sellers in the market. In such a situation, each individual buyer or seller deals in such a small quantity of the product that no individual buyer or seller can, by his own action, affect the price of the product. The individual firm under perfect competition has to take the market price as given, it cannot affect it, it has to adjust its output accordingly to earn maximum profits. In other words, a firm under perfect competition is a price - taker and not a price - maker.
- Homogeneous Product : Each of the firms in a perfectly competitive industry must be making a product which is accepted by customers as being identical or homogeneous with that made by all other firms in the industry. The consumers buy not just out of a deliberate choice but according to the law of probability. This ensures that no firm can charge a price even slightly above the ruling market price, because if it does so, it will lose all its customers.
- Free Entry and Free Exit for Firms : Perfect competition requires that there should be complete freedom for firms to enter the industry or leave the industry whenever they choose to do so. If existing firms are making supernormal profits then in the long run new firms will enter the industry to compete away these profits. If, on the other hand, firms are making losses then, some of the existing firms will leave the industry in the long run with the result that the price of the product will rise and the remaining firms which are left in the industry will be earning normal profits.
- Perfect Knowledge : The fourth condition of perfection competition is the existence of perfect knowledge on the part of buyers and sellers about market conditions, there is no need to incur any expenditure on publicity and advertisement; nor can any seller charge a higher price than the prevailing price because in that case the buyers will shift to some other sellers. Similarly, the sellers also have a perfect knowledge of potential sales at various price levels and also perfect knowledge of cost behaviour. The producers under perfect competition must have complete information regarding alternate employment possibilities of resources and also of profit levels in different industries.
- Perfect Mobility of Factors of Production : This is important condition of perfect competition relates to the perfect mobility of factors of production. This implies that the various factors of production move freely from one occupation to another occupation, from one place to another place and from one use to another use. If in any particular industry, the reward is not adequate. The factors will move out of that industry and enter another industry where they get adequate remuneration.
- Non-existence of Transport Costs : Again, when there is perfect competition in the market, there are no transport costs in carrying a product from one place to another. This condition is very essential because only then there will prevail a single uniform price for the same product. If transport costs are added to the price of the product, even a homogeneous commodity will have different prices depending upon transport costs from the place of supply.
CONTINUE READING
What is Perfect Competition in Economics
Large Number of Buyers and Sellers
Homogeneous Product
Free Entry and Free Exit for Firms
Perfect Knowledge
Perfect Mobility of Factors of Production
Non-existence of Transport Costs
Economics- Perfect Competition.
Kinnari
Tech writer at NewsandStory
